Semantics
Assalamu'laikum.wr.wb my brothers...i'm so sorry, because i'm late to post to you about our lesson. This lesson becomes in the end of Introduction of Linguistics lesson and now, i want to tell you about it.
Semantic is one of branch of lingustics and study the meaning. There are many branch of semantics, namely: polysemy, synonymy,antonymy,hyponymy and idiom. Be based on definition of Charles (2002:3) “semantics was the systematic study of meaning, and semantics was the study of how languages organized and expressed meaning. It referred how language was formed and produced meaning which will bring us to meaning concept”. Therefore, the goal of semantic study was to explain how sequences of languages were matched with their proper meanings and placed in certain environments by speakers of the language. It means that semantics was not just how to build words or sentences and produced language but also how to interpret the language it self.
Under the subject
of semantics we shall deal with the following areas of interest :
1.
The fact that a word can have more than one
meaning, for example ball can be both a dance and around objectfor bouncing
2.
The fact thatdifferent words appear to have the
same meaning, for example ‘regal’ and ‘royal’ or ‘big’ and ‘large’
3.
The fact that some words can b analysed into
components such as adult,female,for example mare implies both adult and female
as well as horse
4.
The fact that some words seems to have
opposites, for example ‘long’ and ‘short’, ‘good’ and ‘bad’ but not ‘desk’ or
‘table’
5.
The fact that the meaning of some words are
included in the meaning of others, for example the meaning of ‘vegetable’ is
included in that of ‘potato’ and the meaning of ‘tree’ is included In that of
‘elm’
6.
The fact that certain combinations of words have
meanings which are very different from
the combination of their separate meanings, for example the meaning of ‘pass’
plus the meanings of ‘on’ do not add up to the meaning of ‘die’ although that
is what ‘pass on’ can mean.
The Branches of semantics
Polysemy
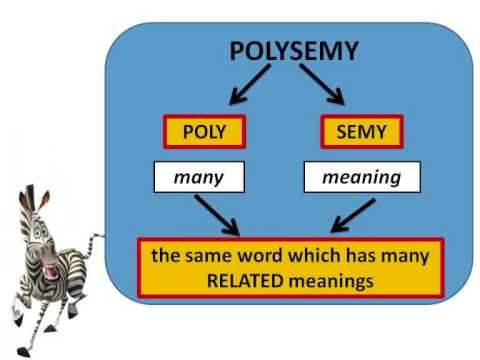

The same
morphological word may have a range of different meanings as a glance at any
dictionary will reveal. Polysemy, meaning “many mening”, is the name given to
the study of this particular phenomeon. If we look up the word ‘star’ of
conscise oxford dictionary, we find the meanings:
·
Celestial body
·
Thing suggesting star by its shape
·
Principal actor or actress in a company
·
(in card game) additional life bought by player
whose lives are lost
Synonymy

Synonymy is the relationship in which two or more words are in
free variation in all or most contexts. The closet we come to absolute synonymy
is when it belong to different dialecs as with:
British
usage us usage
Autumn fall
Estate agent realtor
pavement sidewalk
Antonymy
This is the general term applied to
the sense relationinvilving oppositeness of meaning. For our purposes, it will
be convenient to distinguish three types of ‘oppositeness’, namely (1)
implicitly graded antonyms. (2) complementarity and (3)converseness.

1. Implicitly
graded antonyms refer to pairs of items
such as ‘big’ and small’, ‘good’ and ‘bad’, ‘young’and ‘old’. In orther words,
‘big’, ‘good’ and’young’ can only be interpreted in terms of being ’bigger’,better’
or ‘younger’ than something which is established as thenorm for the comparison.
2. Complementarity
refers to the existenceof such pairs as ‘male’ and ‘female’. It is chrcteristic
of such pairs that the denialof one implies the assertion of the other. Thus if
one is not male, then one is certainly female. Notice the difference between
gradedantonys of the ‘good’/’bad’ typeand complementary pairs. To say :
John is not
single.
Implies:
John is married.
But to say :
John is not bad.
Does not imply:
John is good.
3. Converseness
is the relationship that holds between such related pairs of sentences as:
John sold it to
me
And:
I bought it from
jhon.
Where ‘sell’ and
‘buy’ are in a converse relationship. English has a number of conversely
relatedverbs and so sentence converseness is a common phenomenon:
Jhon lent the
money to peter.
Peter borrowed
the money from jhon.
Hyponymy

Hyponymy is
related to complementarity and incompatibility. Whereas the relationship of
implicit denial is called incompatibility, the relationship of implicit
inclusion is called hyponymy. The assertion of
hyponym:
This is a rose.
Implies the
assertion of the superordinate:
This is a flower.
Idiom
An idiom is a
group of words whose meaning cannot be explained in terms of the habitual meanings
of the words that make up the piece of language. Idiom involve the non-literal
use of language and theycan ce categorised as follows:
1.
Alliterative comparisons:
Dead as a dodo
Fit as a fiddle
Good asgold
2.
Noun phrases:
A blind alley(route that leads nowhere, a false trail)
A close shave (a narrow escape)
3.
Prepodition phrases:
At sixes and sevens (unable/unwilling to agree)
By book or by crook (by whatever methods prove
necessary)
4.
Verb + preposition phrase:
Kick the bucket (die)
Pop your clogs (die)
5.
Verb + preposition phrase:
Be inclover (be exceptionally comfortable)
Be in the doghouse (be in disgrace)
6.
Verb + dverb:
Give in (yield)
Put down (kill).
Those our lesson about semantic and it becomes in the end of introduction of linguistics lesson. I hope this blog can help you to know branches of linguistics and don't forget to show to you a video in order you can more understand about semantic..thank you very much and seee you next time brothers (Y)


Comments
Post a Comment